|
SNAP Library , Developer Reference
2013-01-07 14:03:36
SNAP, a general purpose, high performance system for analysis and manipulation of large networks
|
|
SNAP Library , Developer Reference
2013-01-07 14:03:36
SNAP, a general purpose, high performance system for analysis and manipulation of large networks
|
#include <linalg.h>
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | SymetricToTridiag (TFltVV &a, int n, TFltV &d, TFltV &e) |
| static void | EigSymmetricTridiag (TFltV &d, TFltV &e, int n, TFltVV &z) |
| static void | CholeskyDecomposition (TFltVV &A, TFltV &p) |
| static void | CholeskySolve (const TFltVV &A, const TFltV &p, const TFltV &b, TFltV &x) |
| static void | SolveSymetricSystem (TFltVV &A, const TFltV &b, TFltV &x) |
| static void | InverseSubstitute (TFltVV &A, const TFltV &p) |
| static void | InverseSymetric (TFltVV &A) |
| static void | InverseTriagonal (TFltVV &A) |
| static void | LUDecomposition (TFltVV &A, TIntV &indx, double &d) |
| static void | LUSolve (const TFltVV &A, const TIntV &indx, TFltV &b) |
| static void | SolveLinearSystem (TFltVV &A, const TFltV &b, TFltV &x) |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| static double | sqr (double a) |
| static double | sign (double a, double b) |
| static double | pythag (double a, double b) |
| static void | nrerror (const TStr &error_text) |
| void TNumericalStuff::CholeskyDecomposition | ( | TFltVV & | A, |
| TFltV & | p | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 786 of file linalg.cpp.
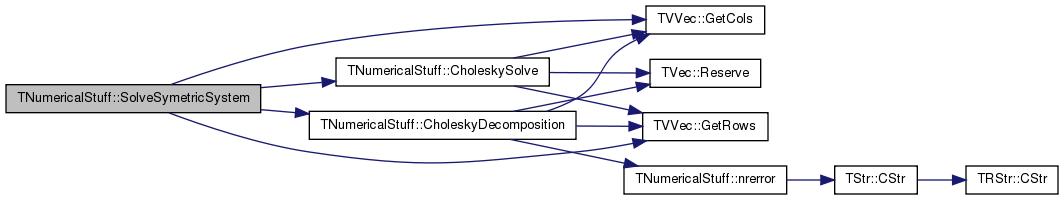
References Assert, TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), nrerror(), and TVec< TVal >::Reserve().
Referenced by InverseSymetric(), and SolveSymetricSystem().
{
Assert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
int n = A.GetRows(); p.Reserve(n,n);
int i,j,k;
double sum;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {
for (j=i;j<=n;j++) {
for (sum=A(i-1,j-1),k=i-1;k>=1;k--) sum -= A(i-1,k-1)*A(j-1,k-1);
if (i == j) {
if (sum <= 0.0)
nrerror("choldc failed");
p[i-1]=sqrt(sum);
} else A(j-1,i-1)=sum/p[i-1];
}
}
}
| void TNumericalStuff::CholeskySolve | ( | const TFltVV & | A, |
| const TFltV & | p, | ||
| const TFltV & | b, | ||
| TFltV & | x | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 804 of file linalg.cpp.
References TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), IAssert, and TVec< TVal >::Reserve().
Referenced by SolveSymetricSystem().
{
IAssert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
int n = A.GetRows(); x.Reserve(n,n);
int i,k;
double sum;
// Solve L * y = b, storing y in x
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {
for (sum=b[i-1],k=i-1;k>=1;k--)
sum -= A(i-1,k-1)*x[k-1];
x[i-1]=sum/p[i-1];
}
// Solve L^T * x = y
for (i=n;i>=1;i--) {
for (sum=x[i-1],k=i+1;k<=n;k++)
sum -= A(k-1,i-1)*x[k-1];
x[i-1]=sum/p[i-1];
}
}

| void TNumericalStuff::EigSymmetricTridiag | ( | TFltV & | d, |
| TFltV & | e, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| TFltVV & | z | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 729 of file linalg.cpp.
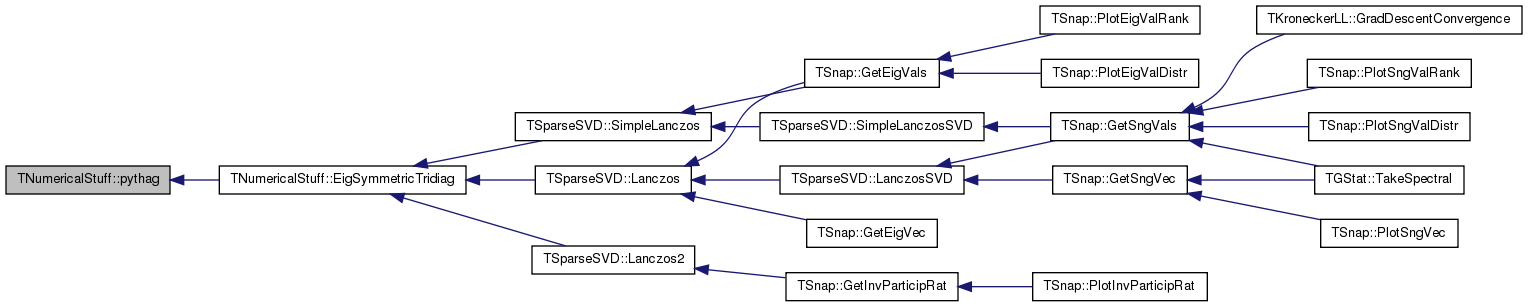
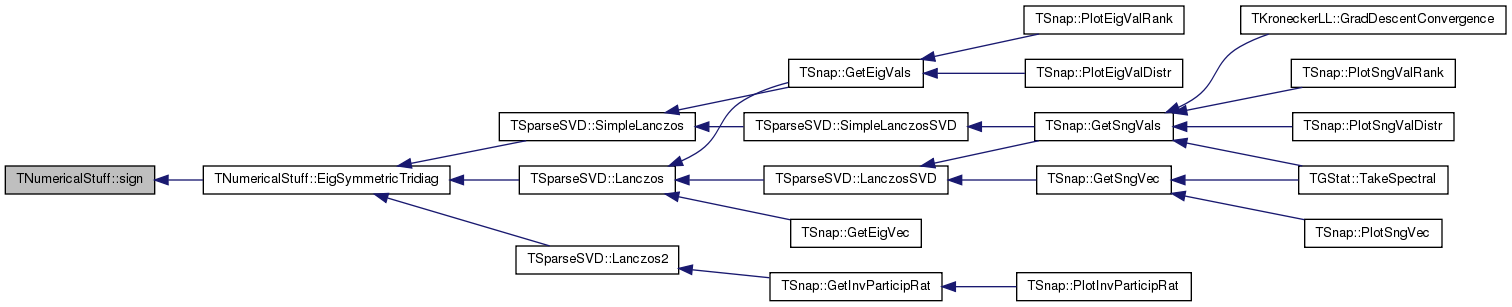
References TFlt::Abs(), nrerror(), pythag(), and sign().
Referenced by TSparseSVD::Lanczos(), TSparseSVD::Lanczos2(), and TSparseSVD::SimpleLanczos().
{
int m,l,iter,i,k; // N = n+1;
double s,r,p,g,f,dd,c,b;
// Convenient to renumber the elements of e
for (i=2;i<=n;i++) e[i-1]=e[i];
e[n]=0.0;
for (l=1;l<=n;l++) {
iter=0;
do {
// Look for a single small subdiagonal element to split the matrix.
for (m=l;m<=n-1;m++) {
dd=TFlt::Abs(d[m])+TFlt::Abs(d[m+1]);
if ((double)(TFlt::Abs(e[m])+dd) == dd) break;
}
if (m != l) {
if (iter++ == 60) nrerror("Too many iterations in EigSymmetricTridiag");
//Form shift.
g=(d[l+1]-d[l])/(2.0*e[l]);
r=pythag(g,1.0);
//This is dm - ks.
g=d[m]-d[l]+e[l]/(g+sign(r,g));
s=c=1.0;
p=0.0;
// A plane rotation as in the original QL, followed by
// Givens rotations to restore tridiagonal form
for (i=m-1;i>=l;i--) {
f=s*e[i];
b=c*e[i];
e[i+1]=(r=pythag(f,g));
// Recover from underflow.
if (r == 0.0) {
d[i+1] -= p;
e[m]=0.0;
break;
}
s=f/r;
c=g/r;
g=d[i+1]-p;
r=(d[i]-g)*s+2.0*c*b;
d[i+1]=g+(p=s*r);
g=c*r-b;
// Next loop can be omitted if eigenvectors not wanted
for (k=0;k<n;k++) {
f=z(k,i);
z(k,i)=s*z(k,i-1)+c*f;
z(k,i-1)=c*z(k,i-1)-s*f;
}
}
if (r == 0.0 && i >= l) continue;
d[l] -= p;
e[l]=g;
e[m]=0.0;
}
} while (m != l);
}
}
| void TNumericalStuff::InverseSubstitute | ( | TFltVV & | A, |
| const TFltV & | p | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 832 of file linalg.cpp.
References TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), and IAssert.
Referenced by InverseSymetric().
{
IAssert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
int n = A.GetRows(); TFltV x(n);
int i, j, k; double sum;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// solve L * y = e_i, store in x
// elements from 0 to i-1 are 0.0
for (j = 0; j < i; j++) x[j] = 0.0;
// solve l_ii * y_i = 1 => y_i = 1/l_ii
x[i] = 1/p[i];
// solve y_j for j > i
for (j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
for (sum = 0.0, k = i; k < j; k++)
sum -= A(j,k) * x[k];
x[j] = sum / p[j];
}
// solve L'* x = y, store in upper triangule of A
for (j = n-1; j >= i; j--) {
for (sum = x[j], k = j+1; k < n; k++)
sum -= A(k,j)*x[k];
x[j] = sum/p[j];
}
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) A(i,j) = x[j];
}
}

| void TNumericalStuff::InverseSymetric | ( | TFltVV & | A | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 861 of file linalg.cpp.
References CholeskyDecomposition(), TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), IAssert, and InverseSubstitute().
{
IAssert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
TFltV p;
// first we calculate cholesky decomposition of A
CholeskyDecomposition(A, p);
// than we solve system A x_i = e_i for i = 1..n
InverseSubstitute(A, p);
}
| void TNumericalStuff::InverseTriagonal | ( | TFltVV & | A | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 870 of file linalg.cpp.
References TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), and IAssert.
{
IAssert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
int n = A.GetRows(); TFltV x(n), p(n);
int i, j, k; double sum;
// copy upper triangle to lower one as we'll overwrite upper one
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i] = A(i,i);
for (j = i+1; j < n; j++)
A(j,i) = A(i,j);
}
// solve
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// solve R * x = e_i, store in x
// elements from 0 to i-1 are 0.0
for (j = n-1; j > i; j--) x[j] = 0.0;
// solve l_ii * y_i = 1 => y_i = 1/l_ii
x[i] = 1/p[i];
// solve y_j for j > i
for (j = i-1; j >= 0; j--) {
for (sum = 0.0, k = i; k > j; k--)
sum -= A(k,j) * x[k];
x[j] = sum / p[j];
}
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) A(j,i) = x[j];
}
}
| void TNumericalStuff::LUDecomposition | ( | TFltVV & | A, |
| TIntV & | indx, | ||
| double & | d | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 898 of file linalg.cpp.
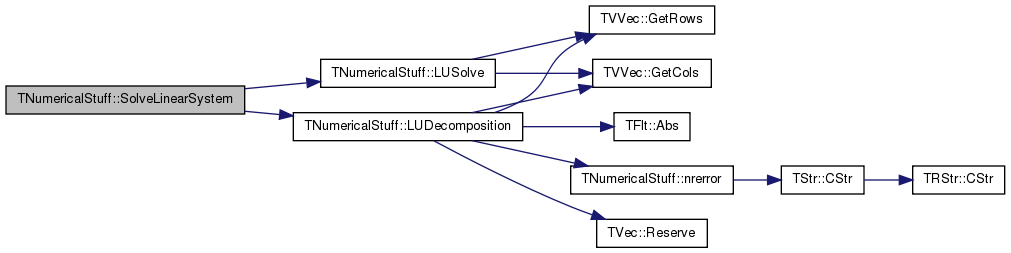
References TFlt::Abs(), Assert, TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), nrerror(), and TVec< TVal >::Reserve().
Referenced by SolveLinearSystem().
{
Assert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
int n = A.GetRows(); indx.Reserve(n,n);
int i=0,imax=0,j=0,k=0;
double big,dum,sum,temp;
TFltV vv(n); // vv stores the implicit scaling of each row.
d=1.0; // No row interchanges yet.
// Loop over rows to get the implicit scaling information.
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {
big=0.0;
for (j=1;j<=n;j++)
if ((temp=TFlt::Abs(A(i-1,j-1))) > big) big=temp;
if (big == 0.0) nrerror("Singular matrix in routine LUDecomposition");
vv[i-1]=1.0/big;
}
for (j=1;j<=n;j++) {
for (i=1;i<j;i++) {
sum=A(i-1,j-1);
for (k=1;k<i;k++) sum -= A(i-1,k-1)*A(k-1,j-1);
A(i-1,j-1)=sum;
}
big=0.0; //Initialize for the search for largest pivot element.
for (i=j;i<=n;i++) {
sum=A(i-1,j-1);
for (k=1;k<j;k++)
sum -= A(i-1,k-1)*A(k-1,j-1);
A(i-1,j-1)=sum;
//Is the figure of merit for the pivot better than the best so far?
if ((dum=vv[i-1] * TFlt::Abs(sum)) >= big) {
big=dum;
imax=i;
}
}
//Do we need to interchange rows?
if (j != imax) {
//Yes, do so...
for (k=1;k<=n;k++) {
dum=A(imax-1,k-1);
A(imax-1,k-1)=A(j-1,k-1); // Tadej: imax-1,k looks wrong
A(j-1,k-1)=dum;
}
//...and change the parity of d.
d = -d;
vv[imax-1]=vv[j-1]; //Also interchange the scale factor.
}
indx[j-1]=imax;
//If the pivot element is zero the matrix is singular (at least to the precision of the
//algorithm). For some applications on singular matrices, it is desirable to substitute
//TINY for zero.
if (A(j-1,j-1) == 0.0) A(j-1,j-1)=1e-20;
//Now, finally, divide by the pivot element.
if (j != n) {
dum=1.0/(A(j-1,j-1));
for (i=j+1;i<=n;i++) A(i-1,j-1) *= dum;
}
} //Go back for the next column in the reduction.
}

| void TNumericalStuff::LUSolve | ( | const TFltVV & | A, |
| const TIntV & | indx, | ||
| TFltV & | b | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 963 of file linalg.cpp.
References Assert, TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), and TVVec< TVal >::GetRows().
Referenced by SolveLinearSystem().
{
Assert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
int n = A.GetRows();
int i,ii=0,ip,j;
double sum;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {
ip=indx[i-1];
sum=b[ip-1];
b[ip-1]=b[i-1];
if (ii)
for (j=ii;j<=i-1;j++) sum -= A(i-1,j-1)*b[j-1];
else if (sum) ii=i;b[i-1]=sum;
}
for (i=n;i>=1;i--) {
sum=b[i-1];
for (j=i+1;j<=n;j++) sum -= A(i-1,j-1)*b[j-1];
b[i-1]=sum/A(i-1,i-1);
}
}

| void TNumericalStuff::nrerror | ( | const TStr & | error_text | ) | [static, private] |
Definition at line 644 of file linalg.cpp.
References TStr::CStr().
Referenced by CholeskyDecomposition(), EigSymmetricTridiag(), and LUDecomposition().
{
printf("NR_ERROR: %s", error_text.CStr());
throw new TNSException(error_text);
}

| double TNumericalStuff::pythag | ( | double | a, |
| double | b | ||
| ) | [static, private] |
Definition at line 649 of file linalg.cpp.
References sqr().
Referenced by EigSymmetricTridiag().
{
double absa = fabs(a), absb = fabs(b);
if (absa > absb)
return absa*sqrt(1.0+sqr(absb/absa));
else
return (absb == 0.0 ? 0.0 : absb*sqrt(1.0+sqr(absa/absb)));
}
| double TNumericalStuff::sign | ( | double | a, |
| double | b | ||
| ) | [static, private] |
Definition at line 640 of file linalg.cpp.
Referenced by EigSymmetricTridiag().
{
return b >= 0.0 ? fabs(a) : -fabs(a);
}
| void TNumericalStuff::SolveLinearSystem | ( | TFltVV & | A, |
| const TFltV & | b, | ||
| TFltV & | x | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 983 of file linalg.cpp.
References LUDecomposition(), and LUSolve().
{
TIntV indx; double d;
LUDecomposition(A, indx, d);
x = b;
LUSolve(A, indx, x);
}
| void TNumericalStuff::SolveSymetricSystem | ( | TFltVV & | A, |
| const TFltV & | b, | ||
| TFltV & | x | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 826 of file linalg.cpp.
References CholeskyDecomposition(), CholeskySolve(), TVVec< TVal >::GetCols(), TVVec< TVal >::GetRows(), and IAssert.
{
IAssert(A.GetRows() == A.GetCols());
TFltV p; CholeskyDecomposition(A, p);
CholeskySolve(A, p, b, x);
}
| double TNumericalStuff::sqr | ( | double | a | ) | [static, private] |
Definition at line 636 of file linalg.cpp.
Referenced by pythag().
{
return a == 0.0 ? 0.0 : a*a;
}
| void TNumericalStuff::SymetricToTridiag | ( | TFltVV & | a, |
| int | n, | ||
| TFltV & | d, | ||
| TFltV & | e | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 657 of file linalg.cpp.
References Assert, TFlt::GetStr(), and IAssertR.
{
int l,k,j,i;
double scale,hh,h,g,f;
for (i=n;i>=2;i--) {
l=i-1;
h=scale=0.0;
if (l > 1) {
for (k=1;k<=l;k++)
scale += fabs(a(i-1,k-1).Val);
if (scale == 0.0) //Skip transformation.
e[i]=a(i-1,l-1);
else {
for (k=1;k<=l;k++) {
a(i-1,k-1) /= scale; //Use scaled a's for transformation.
h += a(i-1,k-1)*a(i-1,k-1);
}
f=a(i-1,l-1);
g=(f >= 0.0 ? -sqrt(h) : sqrt(h));
IAssertR(_isnan(g) == 0, TFlt::GetStr(h));
e[i]=scale*g;
h -= f*g; //Now h is equation (11.2.4).
a(i-1,l-1)=f-g; //Store u in the ith row of a.
f=0.0;
for (j=1;j<=l;j++) {
// Next statement can be omitted if eigenvectors not wanted
a(j-1,i-1)=a(i-1,j-1)/h; //Store u=H in ith column of a.
g=0.0; //Form an element of A u in g.
for (k=1;k<=j;k++)
g += a(j-1,k-1)*a(i-1,k-1);
for (k=j+1;k<=l;k++)
g += a(k-1,j-1)*a(i-1,k-1);
e[j]=g/h; //Form element of p in temporarily unused element of e.
f += e[j]*a(i-1,j-1);
}
hh=f/(h+h); //Form K, equation (11.2.11).
for (j=1;j<=l;j++) { //Form q and store in e overwriting p.
f=a(i-1,j-1);
e[j]=g=e[j]-hh*f;
for (k=1;k<=j;k++) { //Reduce a, equation (11.2.13).
a(j-1,k-1) -= (f*e[k]+g*a(i-1,k-1));
Assert(_isnan(a(j-1,k-1)) == 0);
}
}
}
} else
e[i]=a(i-1,l-1);
d[i]=h;
}
// Next statement can be omitted if eigenvectors not wanted
d[1]=0.0;
e[1]=0.0;
// Contents of this loop can be omitted if eigenvectors not
// wanted except for statement d[i]=a[i][i];
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) { //Begin accumulation of transformationmatrices.
l=i-1;
if (d[i]) { //This block skipped when i=1.
for (j=1;j<=l;j++) {
g=0.0;
for (k=1;k<=l;k++) //Use u and u=H stored in a to form PQ.
g += a(i-1,k-1)*a(k-1,j-1);
for (k=1;k<=l;k++) {
a(k-1,j-1) -= g*a(k-1,i-1);
Assert(_isnan(a(k-1,j-1)) == 0);
}
}
}
d[i]=a(i-1,i-1); //This statement remains.
a(i-1,i-1)=1.0; //Reset row and column of a to identity matrix for next iteration.
for (j=1;j<=l;j++) a(j-1,i-1)=a(i-1,j-1)=0.0;
}
}
